In an effort to raise awareness about noise-induced hearing loss, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has tabbed October as “National Protect Your Hearing Month“. The campaign focuses on educating people about the long-term dangers of participating in activities that produce harmful sound levels, such as attending loud entertainment events, listening to music too loudly on headphones, and occupational exposures.
According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), occupational occupational hearing loss is one of the most common work-related illnesses with 22 million US workers exposed to hazardous noise levels at work each year. Repeated exposures to sounds that are 85 A-weighted decibels (dBA) or higher can cause permanent hearing loss and are associated with other problems including ringing in the ears (tinnitus), high blood pressure (hypertension), and cardiovascular disease. Noise can also reduce workers’ awareness of what is happening around them, including signals, alarms, and verbal warnings.
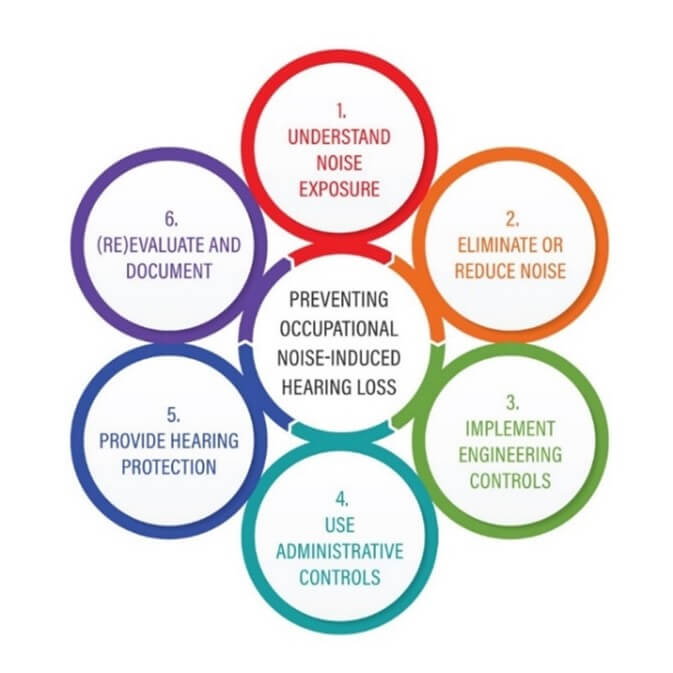
Reducing workplace noise below regulatory and non-regulatory guidance levels (e.g., OSHA PEL, NIOSH REL, and ACGIH TLV) is the best way to prevent occupational hearing loss and other effects from hazardous noise including worker stress and fatigue, increased productivity and better morale, and improved relations with management. By better understanding occupational noise exposures, health and safety professionals, employers, and workers can all help prevent occupational hearing loss.
Employers and employees can learn more about the magnitude, location, frequency, and personal exposure levels to noise within the workplace through a workplace noise survey including area noise survey mapping and personal noise dosimetry.
Employees with noise exposures equal to or exceeding the OSHA Action Level at 85 dBA 8-hr time weighted average (TWA) must be included in a Hearing Conservation Program (HCP). The elements of a HCP include monitoring employee noise exposures, implementing feasible engineering, administrative and work practice controls, providing each overexposed employee with individually fitted hearing protected with an adequate nose reduction rating (NRR), training employees on noise hazards and protection measures, measuring employee baseline and annual audiometry, and keeping records such as exposure measurements and audiometric test results.
RHP Risk Management’s Industrial Hygienists perform facility and environmental noise assessments and mapping. RHP’s experience spans across a variety of work environments including manufacturing, construction, agricultural and entertainment. We provide solutions to reduce employee noise exposures to achieve regulatory and non-regulatory compliance that are effective, achievable and manageable. Contact RHP Risk Management at (866) 481-8188 to learn more about our workplace noise consulting and testing services.